Por favor, use este identificador para citar o enlazar a este item:
http://hdl.handle.net/10261/3081COMPARTIR / EXPORTAR:
 SHARE SHARE
 CORE
BASE CORE
BASE
|
|
| Visualizar otros formatos: MARC | Dublin Core | RDF | ORE | MODS | METS | DIDL | DATACITE | |

| Título: | Isolation, cloning and structural characterisation of boophilin, a multifunctional kunitz-type proteinase inhibitor from the cattle tick |
Autor: | Macedo-Ribeiro, Sandra; Almeida, Carla; Calisto, Bárbara M. CSIC ORCID; Friedrich, Thomas; Mentele, Reinhard; Stürzebecher, Jörg; Fuentes Prior, Pablo; Pereira, Pedro José Barbosa | Fecha de publicación: | 20-feb-2008 | Editor: | Public Library of Science | Citación: | 2008, PLoS ONE. 2008 Feb 20;3(2):e1624. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001624 |
Resumen: | Inhibitors of coagulation factors from blood-feeding animals display a wide variety of structural motifs and inhibition mechanisms. We have isolated a novel inhibitor from the cattle tick Boophilus microplus, one of the most widespread parasites of farm animals. The inhibitor, which we have termed boophilin, has been cloned and overexpressed in Escherichia coli. Mature boophilin is composed of two canonical Kunitz-type domains, and inhibits not only the major procoagulant enzyme, thrombin, but in addition, and by contrast to all other previously characterised natural thrombin inhibitors, significantly interferes with the proteolytic activity of other serine proteinases such as trypsin and plasmin. The crystal structure of the bovine alpha-thrombin.boophilin complex, refined at 2.35 A resolution reveals a non-canonical binding mode to the proteinase. The N-terminal region of the mature inhibitor, Q16-R17-N18, binds in a parallel manner across the active site of the proteinase, with the guanidinium group of R17 anchored in the S(1) pocket, while the C-terminal Kunitz domain is negatively charged and docks into the basic exosite I of thrombin. This binding mode resembles the previously characterised thrombin inhibitor, ornithodorin which, unlike boophilin, is composed of two distorted Kunitz modules. Unexpectedly, both boophilin domains adopt markedly different orientations when compared to those of ornithodorin, in its complex with thrombin. The N-terminal boophilin domain rotates 9 degrees and is displaced by 6 A, while the C-terminal domain rotates almost 6 degrees accompanied by a 3 A displacement. The reactive-site loop of the N-terminal Kunitz domain of boophilin with its P(1) residue, K31, is fully solvent exposed and could thus bind a second trypsin-like proteinase without sterical restraints. This finding explains the formation of a ternary thrombin.boophilin.trypsin complex, and suggests a mechanism for prothrombinase inhibition in vivo. | URI: | http://hdl.handle.net/10261/3081 | DOI: | 10.1371/journal.pone.0001624 | ISSN: | 1932-6203 |
| Aparece en las colecciones: | (CIC) Artículos |
Ficheros en este ítem:
| Fichero | Descripción | Tamaño | Formato | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| isolation.pdf | Main text | 1,1 MB | Adobe PDF |  Visualizar/Abrir |
| isolation_s001.tiff | Figure S1. Mass spectrum of affinity-purified native boophilin obtained using MALDI-TOF. | 797,59 kB | TIFF | 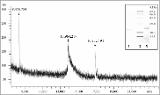 Visualizar/Abrir |
| isolation_s002.tiff | Figure S2. Two-domain Kunitz inhibitors of thrombin display different surface potentials. | 3,12 MB | TIFF | 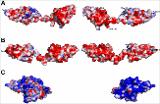 Visualizar/Abrir |
| isolation_s003.doc | Table S1. Amino acid sequences of peptides derived from purified native boophilin. | 29 kB | Microsoft Word | Visualizar/Abrir |
| isolation_s004.doc | Table S2. Oligonucleotides used for boophilin cloning. | 28 kB | Microsoft Word | Visualizar/Abrir |
CORE Recommender
PubMed Central
Citations
42
checked on 24-abr-2024
SCOPUSTM
Citations
101
checked on 24-abr-2024
WEB OF SCIENCETM
Citations
95
checked on 26-feb-2024
Page view(s)
457
checked on 26-abr-2024
Download(s)
444
checked on 26-abr-2024
Google ScholarTM
Check
Altmetric
Altmetric
Artículos relacionados:
NOTA: Los ítems de Digital.CSIC están protegidos por copyright, con todos los derechos reservados, a menos que se indique lo contrario.
